
Anatomy Of A Worm
470221-930 External Anatomy Incisions for Dissection Lay the worm dorsal side up. Pin the cranial and caudal ends. Incise beyond the clitellum, then extend the cut to both ends, from the middle out. Take great care to cut no more than 1/16 of an inch deep into the worm. With forceps, grasp the edges of the skin carefully.
 Rick Kollath.jpg)
Life cycle of an earthworm Earthworm Society of Britain
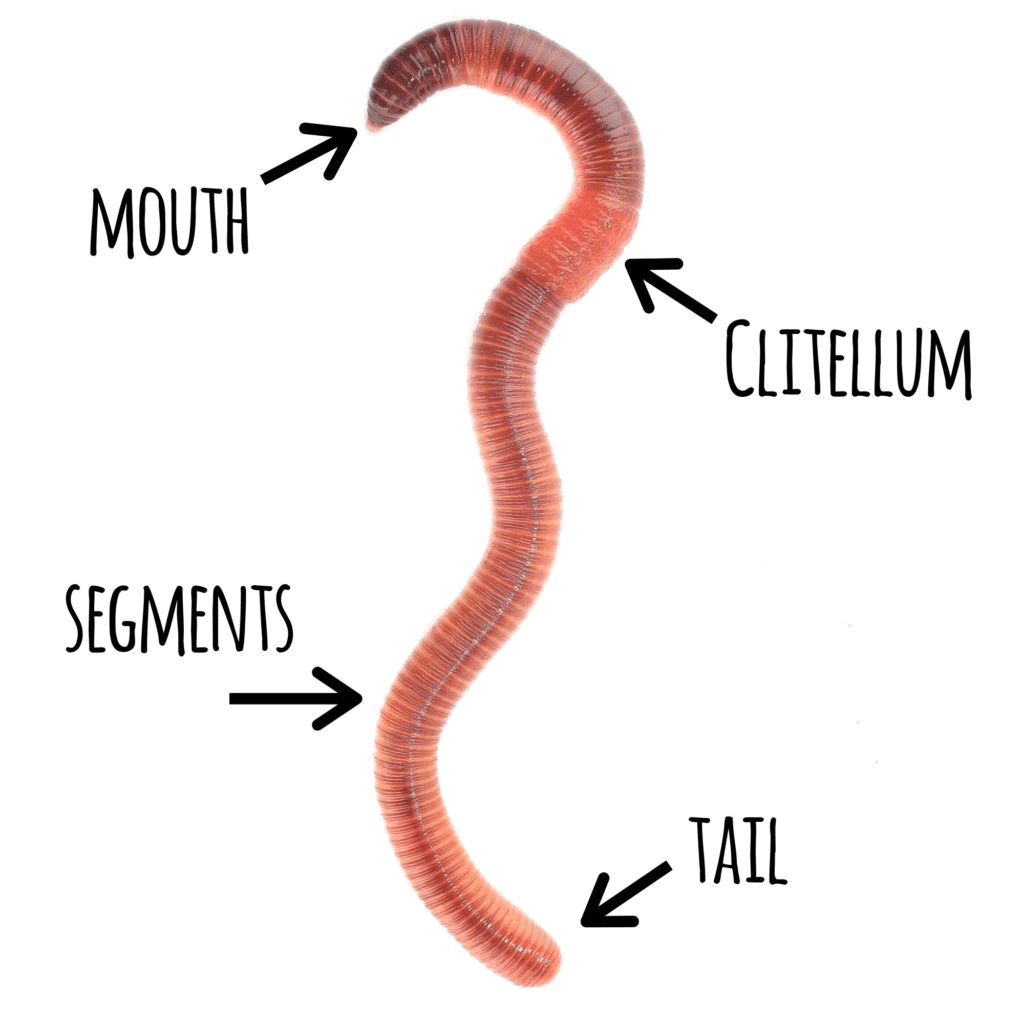
The earthworm body is divided into ringlike segments (as many as 150 in L. terrestris).Some internal organs, including the excretory organs, are duplicated in each segment. Between segments 32 and 37 is the clitellum, a slightly bulged, discoloured organ that produces a cocoon for enclosing the earthworm's eggs.The body is tapered at both ends, with the tail end the blunter of the two.

Worm Diagrams Labeled Images and Photos finder
Earthworm Dissection Guide Earthworms are important helpers in the garden or field! Their tunneling mixes up the soil and brings rich soil to the surface. Our earthworm anatomy and dissection guide will walk you through the entire process. Earthworm Observation: External Anatomy Click for full-size pdf

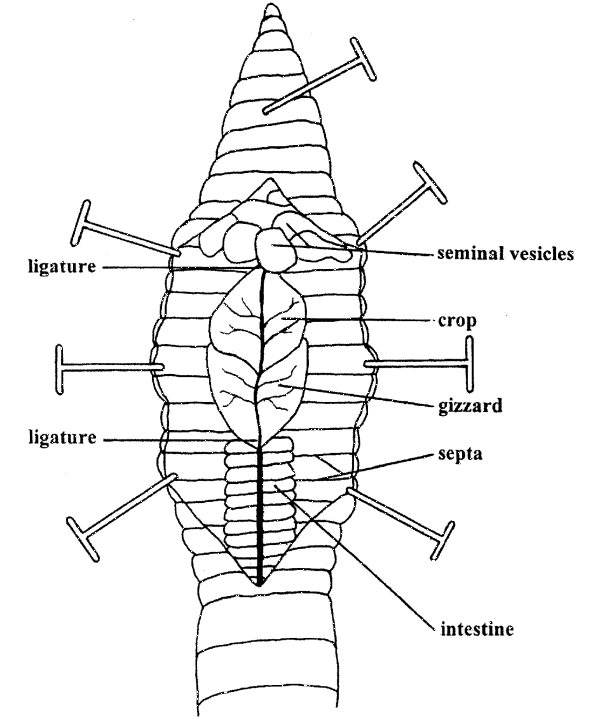
53. Lumbricus terrestris (Lumbricidae). A. External features of worm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida.The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta.In classical systems, they were in the order of Opisthopora since the male pores opened posterior to the female pores, although the internal male segments are anterior to the female.

2. Schematic of earthworm process of mating and reproduction
External Anatomy. Examine your earthworm and determine the dorsal and ventral sides. Locate the clitellum which is on the anterior end of the worm. Locate the mouth of the worm on the far anterior end of the worm.The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts. The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae.
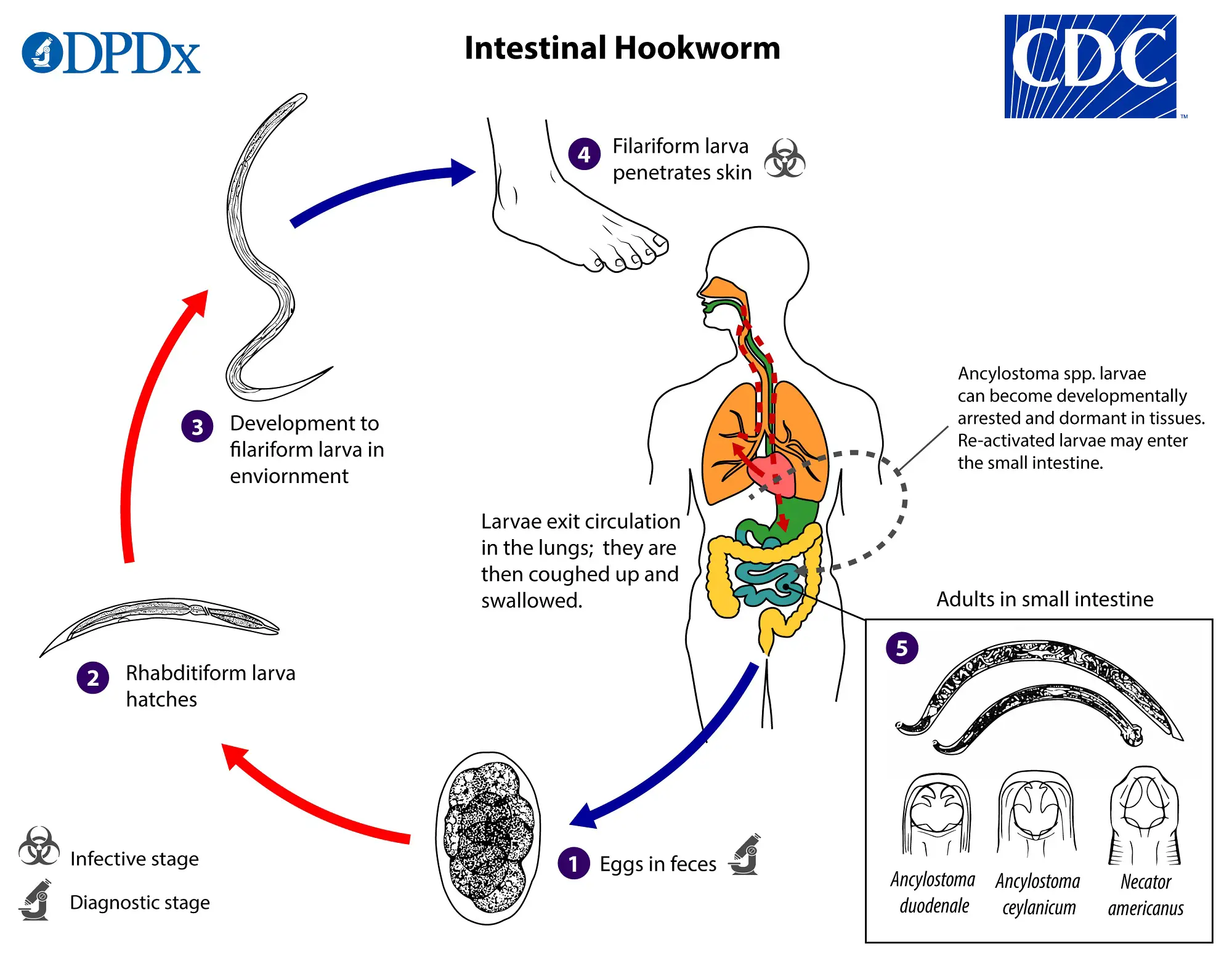
Hookworm Characteristics, Life Cycle, Pathogenesis and Diagnosis
Scientific Name: Lumbricus terrestris Type: Invertebrates Diet: Herbivore Average Life Span In The Wild: Up to 6 years Size: Up to 14 inches Weight: Up to 0.39 ounces Earthworms do not live in.
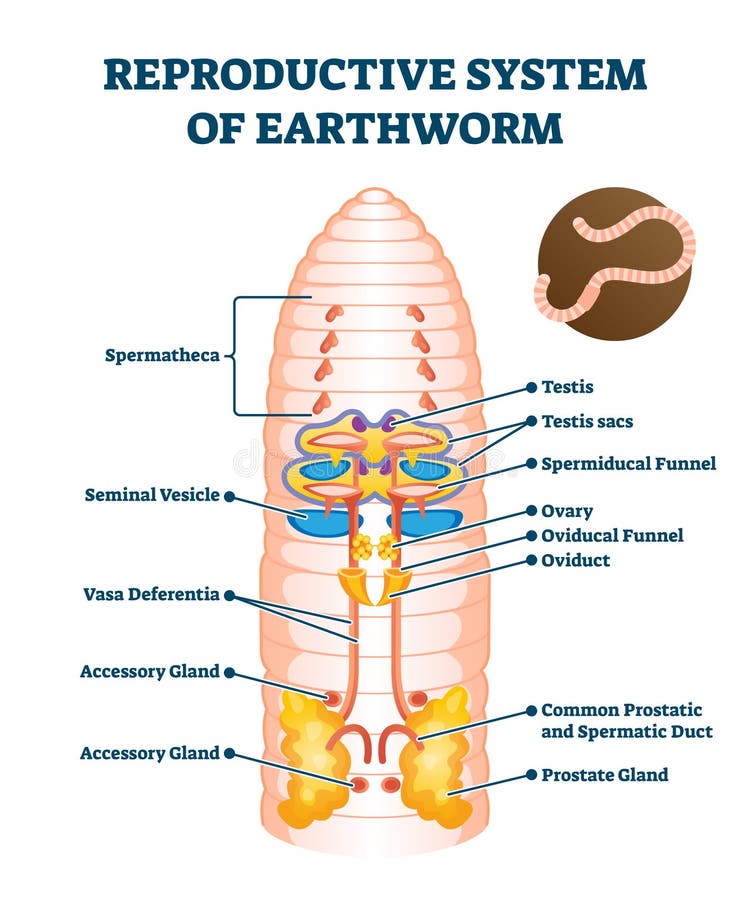
Reproductive System of Anatomical Earthworm Labeled Scheme Vector
Objectives: In this earthworm dissection guide, you will learn to: • Describe the appearance of various organs found in the earthworm. • Name the organs that make up various systems of the earthworm. Materials:
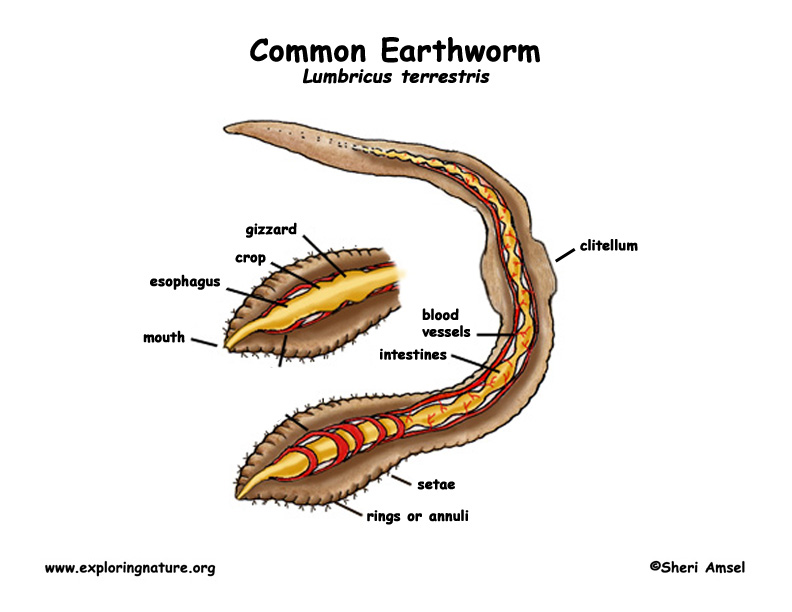
Earthworm
Earthworm Digestive System Diagram (Image Will Be Uploaded Soon) Physiology of Digestion.. Worms position up in the opposite directions and share sperm from the clitellum, which is a thickened glandular band present at the anterior end of adult worms. The clitellum creates a thick mucus ring after mating, which solidifies and forms the.
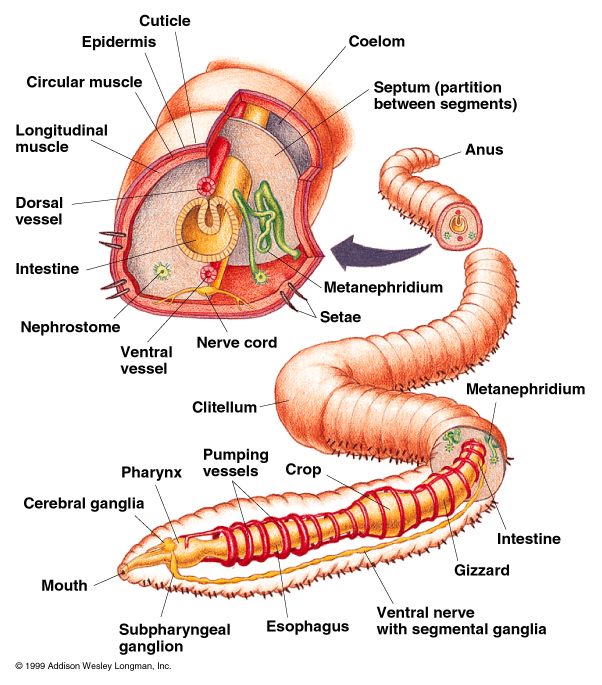
Annelida diagram Earthworms, Worm farm, Annelid
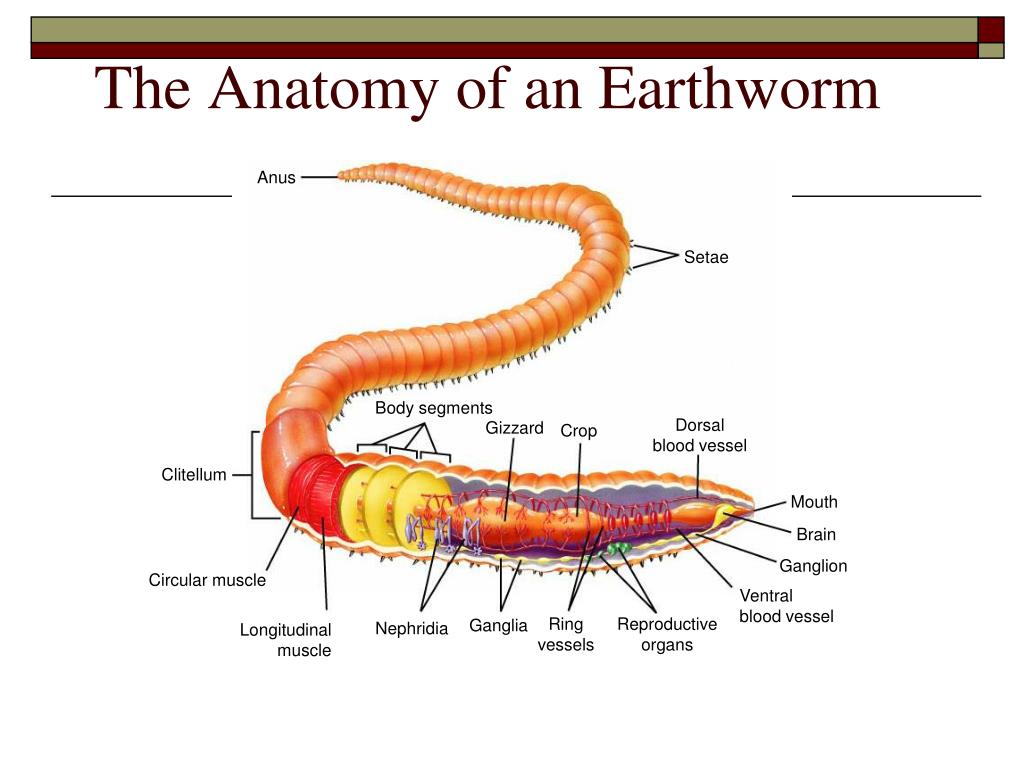
Morphology of Earthworm. Earthworms have a reddish brown color with a cylindrical body. The body is also elongated and is pointed in the anterior region, while the posterior region is rounded. The body is segmented and there are about 100 to 120 metameres or short segments. There is a dark median mid-dorsal blood vessel that is seen on the.

Figure 33.23 Anatomy of an earthworm
Diagram of an Earthworm Morphology of Earthworm [Click Here for Sample Questions] Earthworms are reddish-brown in colour and have a cylindrical body. The body is also elongated and pointed in the anterior region, with a rounded posterior region. The body is segmented, with approximately 100 to 120 metameres, or short segments.
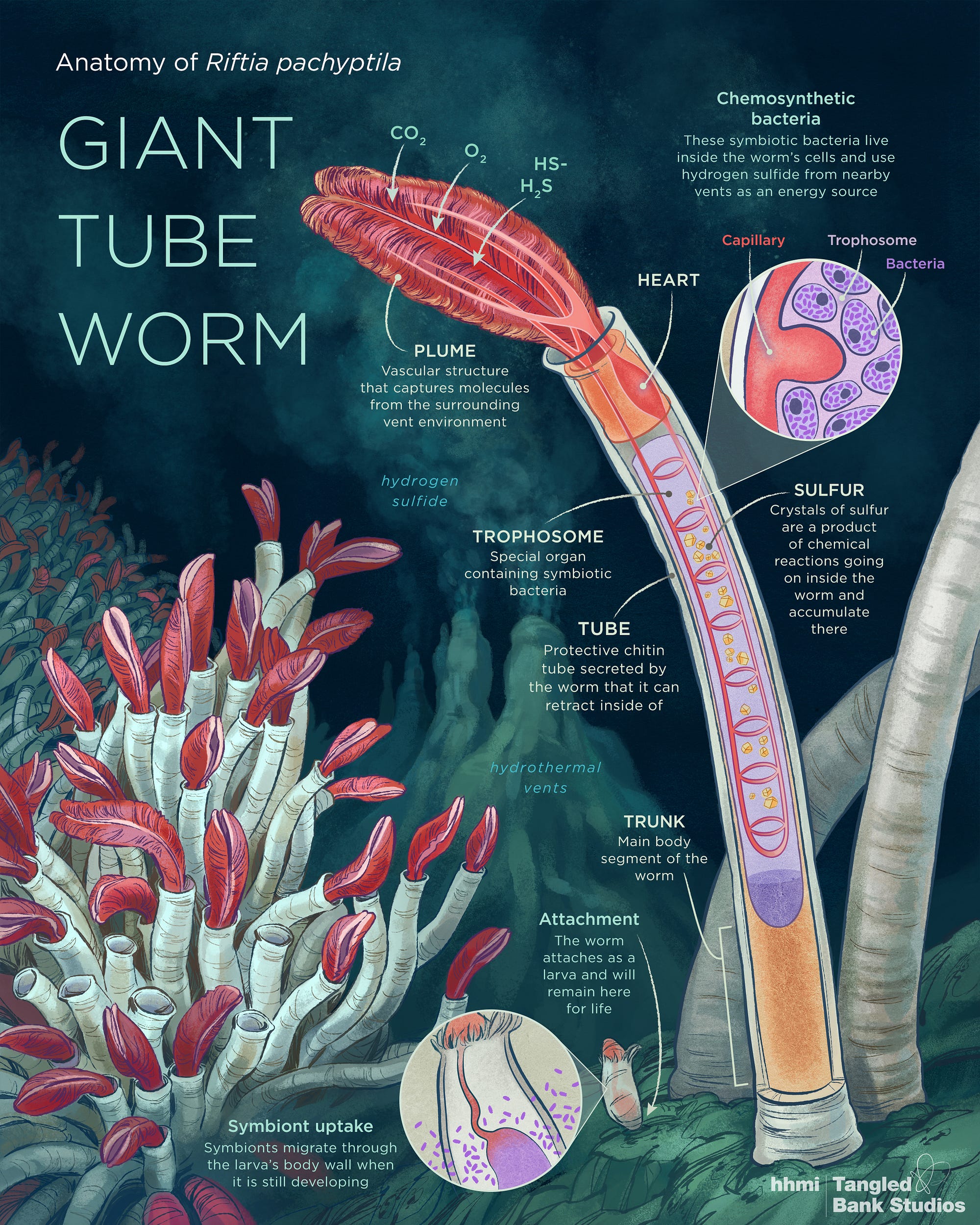
Anatomy of a Giant Tube Worm I Contain Multitudes Medium
Size can be established by using the size chart on the General Earthworm Diagram to decide whether you have a small, medium or large adult.To determine the length of your earthworm, Allow the worm to freely extend itself as if it was crawling; Measure the maximum distance the earthworm covers when completely stretched out.

Worm Diagrams Labeled
Yes! This is where their mouth is found - it's usually located at their head end. The mouth is used for feeding and collecting food. What Else Do Worms Have? Worms have a digestive system, circulatory system, nervous system, and also reproductive organs. The Digestive System Of A Worm
The Life Cycle of a Worm Mindful Waste
The following diagram of the earthworm depicts its morphological features:-(Image will be uploaded soon) Morphology of Earthworm. Earthworms possess a segmented tube-shaped body that is reddish-brown in colour. The body is precisely divided into small segments. The dorsal side holds a dark line of blood vessels whereas the ventral side.
Earthworm Dissection
Worm Anatomy. A worms body is made up of many segments called 'annuli'. The length of a worms body has muscles which contract and relax which enables the worm to move along a surface. The 'annuli' are covered in tiny hairs called 'setae' which help the worms movement. Worms have no lungs, so they do not breathe like a human being or.

labelled diagram of earthworm Sustainableced
Ana Cope Earthworms are beneficial to the soil ecosystem as they help modify the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil. These organisms recycle and decompose organic materials,.
PPT Three Phyla of Worms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Earthworm Anatomy Diagram. To understand a worm anatomy and physical functions it is also a good idea to understand its purpose and function in nature. It truly plays a huge role in the creation and design of our ecosystem. A worm has three major duties in life eat, poop, and mate.